CATCHING COLON CANCER EARLY

Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, is one of the most common cancers worldwide. Fortunately, early detection through regular screening can significantly increase survival rates. In this article, we will discuss the importance of early detection, review various screening methods, and highlight the benefits of regular screenings.
THE IMPORTANCE OF EARLY DETECTION OF COLON CANCER

Early detection of colorectal cancer is crucial because it allows for treatment before the disease progresses to more advanced stages. According to the American Cancer Society (ACS), when detected early, colorectal cancer is highly treatable, with a five-year survival rate of over 90% for those diagnosed at the localized stage. However, if the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, the survival rate drops significantly (American Cancer Society, 2023).
Firstly, colorectal cancer often develops without noticeable symptoms in its early stages. By the time symptoms appear, the cancer may have already advanced. Therefore, relying on symptoms alone is not a reliable way to detect colorectal cancer early. This is where regular screening comes into play. Screening helps identify cancer or precancerous conditions before symptoms develop, allowing for earlier intervention and treatment.
SCREENING METHODS FOR COLON CANCER
Several screening methods are available, each with its own advantages and limitations. These methods include colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, and stool tests. Understanding each method can help individuals make informed decisions about their screening options.
Colonoscopy
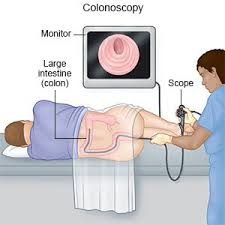
Colonoscopy is a comprehensive screening method that examines the entire colon and rectum using a flexible tube equipped with a camera. During the procedure, a gastroenterologist can view the lining of the colon on a monitor and remove any suspicious polyps for further examination. According to the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), colonoscopy is recommended every ten years for individuals at average risk starting at age 45 (USPSTF, 2022).
The main advantage of colonoscopy is its ability to detect and remove polyps during the same procedure. Polyps are growths on the inner lining of the colon that can turn into cancer over time. By removing them, colonoscopy not only detects cancer but also prevents it from developing. However, the procedure requires bowel preparation and sedation, which some people might find uncomfortable.
Sigmoidoscopy
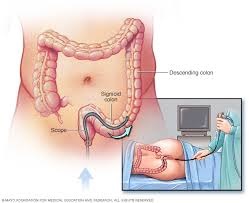
Sigmoidoscopy is similar to colonoscopy but examines only the rectum and lower part of the colon. This method involves a shorter, flexible tube and generally requires less preparation compared to a full colonoscopy. The USPSTF recommends sigmoidoscopy every five years for those at average risk, often in combination with stool tests (USPSTF, 2022).
While sigmoidoscopy is less invasive and quicker than a colonoscopy, it does not examine the entire colon. Therefore, if abnormalities are found, a follow-up colonoscopy might be necessary. Despite this, sigmoidoscopy can still be an effective screening tool, especially for individuals who are hesitant to undergo a full colonoscopy.
Stool Tests

Stool tests are non-invasive methods that detect cancer or precancerous conditions through samples of stool. The main types of stool tests include:
- Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT): This test detects hidden blood in the stool, which can be a sign of cancer or large polyps. FIT is usually done annually.
- Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT): Similar to FIT, FOBT also checks for hidden blood in the stool but may require dietary restrictions before the test. FOBT is generally done annually.
- Stool DNA Test (e.g., Cologuard): This test analyzes stool samples for specific genetic markers associated with colon cancer. It is typically recommended every three years.
Stool tests are convenient and can be done at home. They are less invasive and do not require bowel preparation. However, if a stool test indicates potential issues, a follow-up colonoscopy is usually needed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the appropriate treatment.
BENEFIT OF REGULAR SCREENING OF COLON CANCER
Regular screenings offer several benefits that contribute to better health outcomes and quality of life. Here are some key advantages:
- Early Detection and Treatment:
As mentioned earlier, the primary benefit of regular screenings is the early detection of colon cancer. Early detection often means the cancer is found at a more treatable stage, which can lead to more effective treatment and higher survival rates. For example, localized colon cancer, where the disease has not spread beyond the colon, has a much better prognosis than advanced-stage cancer.
- Prevention of Colon Cancer:
Regular screenings can also help prevent colon cancer by detecting and removing precancerous polyps before they develop into cancer. Studies have shown that screening programs that include polyp removal can reduce the incidence of colon cancer by up to 68% (National Cancer Institute, 2021). This preventive aspect makes screening not just a diagnostic tool but also a proactive approach to cancer prevention.
- Reduced Risk of Advanced Disease:
By identifying cancer early, regular screenings reduce the likelihood of the disease advancing to a stage where treatment becomes more complex and less effective. This not only improves survival rates but also reduces the need for aggressive treatments, which can have significant side effects.
- Peace of Mind:
Undergoing regular screenings provides peace of mind, knowing that any potential issues are being monitored closely. For those with a family history of colon cancer or other risk factors, regular screenings can be especially reassuring. Even if results are not perfect, knowing that you’re taking proactive steps to monitor your health can alleviate anxiety and contribute to overall well-being.
CONCLUSION.
In summary, colorectal cancer screening and early detection play a vital role in combating this prevalent disease. Regular screenings, including colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, and stool tests, offer valuable opportunities to detect colorectal cancer at an early stage, prevent its development, and reduce the risk of advanced disease. By understanding the different screening methods and their benefits, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and take proactive steps to ensure their well-being.
To maximize the benefits of colorectal cancer screening, it is essential to follow the recommended guidelines and consult with healthcare professionals to determine the best approach based on individual risk factors and health conditions. Regular screenings not only improve survival rates but also contribute to a better quality of life by allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
For more information on colon cancer screening guidelines and recommendations, refer to reputable sources such as the American Cancer Society (2023) and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (2022). Taking charge of your health through regular screenings is a powerful way to protect yourself against colon cancer and maintain overall well-being.
REFERENCES
American Cancer Society. (2023). Colorectal Cancer Facts & Figures 2023-2025. Retrieved from American Cancer Society
National Cancer Institute. (2021). Colorectal Cancer Screening. Retrieved from National Cancer Institute
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. (2022). Colorectal Cancer: Screening. Retrieved from USPSTF