UNDERSTANDING LUNG CANCER:SYMPTOMS,CAUSES AND RISK FACTORS
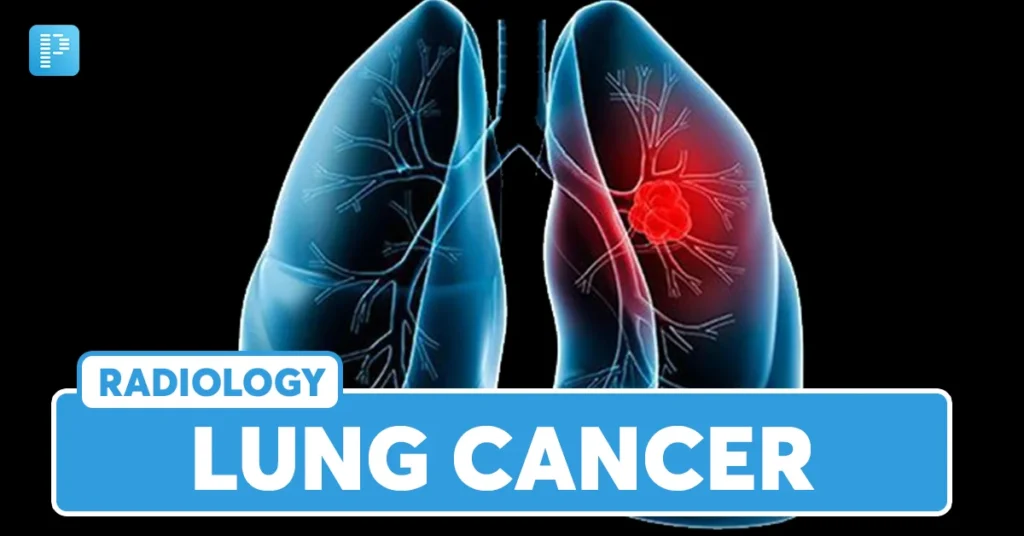
Lung cancer is a serious and often life-threatening condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when abnormal cells in the lungs begin to grow uncontrollably, forming tumors that can interfere with normal lung function. This comprehensive guide aims to provide clear and straightforward information about lung cancer, including its symptoms, causes, and risk factors. By understanding these aspects, individuals can better recognize potential signs and take proactive steps towards prevention and early detection.
WHAT IS LUNG CANCER?
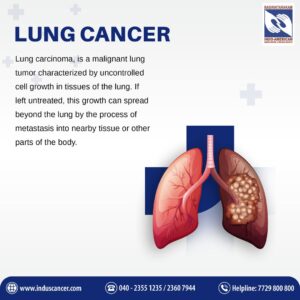
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the lungs. It is classified into two main types based on the appearance of the cancer cells under a microscope: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC is the most common form, accounting for approximately 85% of all lung cancer cases, while SCLC is less common but tends to grow more quickly.
TYPES OF LUNG CANCER
1. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): This type includes several subtypes such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. Each subtype differs in terms of where it starts in the lung and how it spreads.
2. Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): This type of lung cancer is less common but more aggressive. It often starts in the central part of the lungs and can spread rapidly to other parts of the body.
SYMPTOMS OF LUNG CANCER
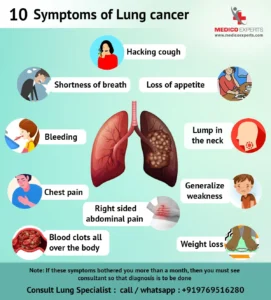
Recognizing the symptoms of lung cancer early can be crucial for effective treatment. However, symptoms often do not appear until the cancer has advanced. Common symptoms of lung cancer include:
Early Symptoms

1. Persistent Cough: A cough that doesn’t go away or worsens over time may be an early sign of lung cancer. It is particularly concerning if it produces blood or rust-colored mucus.
2. Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling short of breath can indicate that the cancer is affecting lung function or causing fluid buildup around the lungs.
3. Chest Pain: Persistent chest pain that is not related to other conditions can be a symptom of lung cancer. This pain may be sharp or dull and might worsen with deep breathing or coughing.
Advanced Symptoms
1. Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss without changes in diet or exercise can be a sign of advanced lung cancer. This is often due to the body’s increased energy demands and the cancer’s effects on appetite.
2. Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or weak, even after adequate rest, can be a symptom of lung cancer. This fatigue is often due to the cancer’s impact on overall health and well-being.
3. Hoarseness: A change in voice or persistent hoarseness can occur if the cancer affects the vocal cords or surrounding structures.
CAUSES OF LUNG CANCER

Understanding the causes of lung cancer is essential for prevention and risk reduction. While the exact cause of lung cancer may not always be clear, several factors are known to increase the risk.
Primary Causes
1. Tobacco Smoking: Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke damage lung cells and increase the risk of developing cancer. Both current and former smokers are at higher risk, and the risk increases with the number of cigarettes smoked over time.
2. Secondhand Smoke: Exposure to secondhand smoke, also known as passive smoke, can also increase the risk of lung cancer. Non-smokers who live with smokers or are frequently in smoky environments are at higher risk.
Other Contributing Factors
1. Exposure to Radon: Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can accumulate in homes and buildings. Long-term exposure to high levels of radon can increase the risk of lung cancer.
2. Occupational Hazards: Certain jobs and industries expose workers to carcinogens that can increase the risk of lung cancer. These include jobs in construction, mining, and manufacturing, where exposure to asbestos, arsenic, or other harmful substances is common.
3. Air Pollution: Long-term exposure to high levels of air pollution, including particulate matter and diesel exhaust, has been linked to an increased risk of lung cancer. Living in areas with poor air quality can contribute to this risk.
RISK FACTORS FOR LUNG CANCER
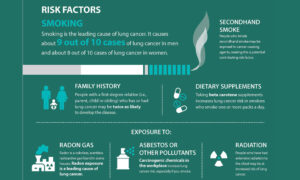
While certain factors increase the likelihood of developing lung cancer, having one or more risk factors does not guarantee that someone will get the disease. Conversely, some people with lung cancer may not have any known risk factors.
Major Risk Factors
1. Age: The risk of lung cancer increases with age. Most people diagnosed with lung cancer are over 65 years old. The cumulative effects of exposure to risk factors over time contribute to this increased risk.
2. Family History: A family history of lung cancer can increase an individual’s risk. Genetic factors and shared environmental exposures may contribute to this increased risk.
3. Previous Lung Conditions: Individuals with a history of certain lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or tuberculosis, may have a higher risk of developing lung cancer.
Modifiable Risk Factors
1. Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is the most effective way to reduce the risk of lung cancer. Even after years of smoking, quitting can significantly lower the risk.
2. Reducing Exposure to Carcinogens: Taking steps to minimize exposure to known carcinogens, such as radon and workplace hazards, can help lower the risk of lung cancer.
DIAGNOSIS AND SCREENING.

Early detection of lung cancer can improve treatment outcomes. Several diagnostic methods and screening options are available.
Diagnostic Methods
1. Imaging Tests: Imaging tests such as chest X-rays and CT scans are commonly used to detect abnormalities in the lungs. These tests can help identify potential tumors and determine their size and location.
2. Biopsy: A biopsy involves taking a small sample of lung tissue to examine it for cancer cells. This procedure can be done using a needle, during a bronchoscopy, or through surgery.
3. Molecular Testing: Molecular testing of tumor samples can help identify specific genetic mutations that may influence treatment options. This testing can provide information on targeted therapies that may be effective.
Screening Options
1. Low-Dose CT Scan: For individuals at high risk of lung cancer, such as long-term smokers, low-dose CT scans are recommended for screening. This test can detect lung cancer at an early stage when treatment may be more effective.
2. Annual Screening: Annual screening with low-dose CT scans is recommended for those who meet specific criteria, such as age and smoking history. Early detection through screening can lead to timely intervention and improved outcomes.
Treatment Options
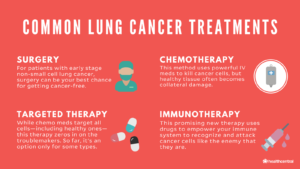
Treatment for lung cancer depends on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient. Various treatment options are available, often used in combination.
Standard Treatments
1. Surgery: Surgery aims to remove the tumor and affected lung tissue. Options include lobectomy (removal of a lobe), pneumonectomy (removal of an entire lung), and wedge resection (removal of a small portion of the lung).
2. Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It is often used for patients who cannot undergo surgery or as an adjuvant treatment to eliminate remaining cancer cells.
3. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. It is commonly used for treating lung cancer that has spread beyond the lungs.
4. Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically target cancer cells with certain genetic mutations. These therapies aim to inhibit the growth of cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells.
5. Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy works by boosting the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. It is a newer treatment option that has shown promise in some cases of lung cancer.
CONCLUSION.
Lung cancer is a complex and serious disease, but understanding its symptoms, causes, and risk factors can play a crucial role in early detection and effective management. Recognizing the symptoms, identifying risk factors, and seeking timely medical attention are essential steps in combating this disease. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can improve their chances of early detection and successful treatment.
For further information and support, consider consulting healthcare professionals and accessing resources from reputable organizations such as the American Cancer Society and the National Cancer Institute.
References:
- American Cancer Society (ACS). (2023). “Lung Cancer Types.” Link
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). (2023). “Types of Lung Cancer.” Link
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). “Lung Cancer Symptoms.” Link
- National Health Service (NHS). (2023). “Lung Cancer Symptoms.” Link
- American Lung Association. (2023). “Causes of Lung Cancer.” Link
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). (2023). “Lung Cancer Risk Factors.” Link
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2023). “Lung Cancer Risk Factors.” Link
- American Cancer Society (ACS). (2023). “Lung Cancer Risk Factors and Prevention.” Link
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). (2023). “Lung Cancer Diagnosis.” Link
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF). (2023). “Lung Cancer Screening Recommendations.” Link
- American Cancer Society (ACS). (2023). “Lung Cancer Treatment.” Link
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). (2023). “Lung Cancer Treatment.” Link
- American Cancer Society (ACS). (2023). “Lung Cancer Overview.” Link
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). (2023). “Lung Cancer.” Link
Written by Fawzi Rufai, Medically Reviewed by Sesan Kareem