Understanding Male Fertility: Factors, Diagnosis, and Treatment
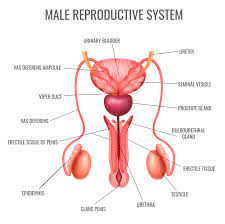
There are many factors that can affect male fertility, including:
- Age. Sperm production decreases with age, so men over the age of 40 are more likely to have fertility problems.
- Genetics. Some men are born with genetic conditions that can affect sperm production or function.
- Medical conditions. Some medical conditions, such as diabetes, can affect male fertility.
- Lifestyle factors. Smoking, drinking alcohol, and using drugs can all affect male fertility.
- Environmental factors. Exposure to certain chemicals or pollutants can also affect male fertility.
Sperm Production
Sperm are produced in the testes through a process called spermatogenesis. It takes about 64-72 days for sperm to fully develop, and the process is influenced by various factors such as hormonal balance, genetic factors, and overall health. Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a crucial role in sperm production.
Sperm Quality
The quality of sperm is determined by several factors, including sperm count, motility (ability to move), morphology (shape and size of sperm), and vitality (percentage of live sperm). These factors collectively contribute to sperm quality, and any abnormalities can affect male fertility.
Factors Affecting Male Fertility
- Age: Advanced paternal age has been associated with a decline in fertility. As men age, the quantity and quality of sperm may decrease, increasing the chances of infertility and genetic abnormalities in offspring.
- Lifestyle and Environmental Factors: Certain lifestyle and environmental factors can have a negative impact on male fertility. These include smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, obesity, exposure to toxins and chemicals, high levels of stress, and prolonged exposure to heat (e.g., hot tubs or saunas).
- Medical Conditions: Various medical conditions can affect male fertility. These include hormonal imbalances (e.g., low testosterone levels), infections (such as sexually transmitted infections), genetic disorders, varicocele (enlarged veins in the testicles), certain medications, and chronic illnesses (e.g., diabetes).
- Sexual Health: Sexual health and function, including erectile dysfunction and ejaculation disorders, can also affect male fertility. Conditions like retrograde ejaculation (where semen enters the bladder instead of being expelled through the penis) or erectile dysfunction may hinder the ability to conceive.
- Diet and Nutrition: A healthy diet that includes essential nutrients such as antioxidants, vitamins (particularly vitamins C and E), zinc, and folate is important for male fertility. Poor nutrition and dietary deficiencies can impact sperm production and quality.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If a couple experiences difficulty conceiving, both partners may undergo fertility evaluations. For men, this typically involves a semen analysis to assess sperm count, motility, morphology, and other factors related to sperm quality. Additional tests may be performed to identify underlying causes of infertility.
Treatment options for male fertility issues vary depending on the underlying cause. In some cases, lifestyle modifications such as quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight can improve fertility. Medical interventions may include hormonal therapies, surgical interventions (e.g., varicocele repair), or assisted reproductive techniques like intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
It is important to note that male fertility is a complex issue, and the chances of conception can vary significantly based on multiple factors. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals specializing in reproductive medicine can provide appropriate diagnosis, treatment, and support for couples facing fertility challenges.
There are a number of things that men can do to improve their fertility, including:
- Maintaining a healthy weight. Being overweight or obese can decrease sperm production.
- Eating a healthy diet. Eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help improve sperm health.
- Getting regular exercise. Exercise can help improve overall health, which can also benefit sperm production.
- Avoiding smoking, drinking alcohol, and using drugs. These substances can all harm sperm production.
- Managing stress. Stress can have a negative impact on sperm production.
- Getting regular checkups. If you are concerned about your fertility, talk to your doctor. There are a number of tests that can be done to assess your fertility.
Delivering your fertility medications on schedule, every time
HubPharm makes it as simple as possible to follow the treatment your doctor recommends. We offer same-day delivery and medication management tools like reminders and auto refills in our app. Our team of patient care pharmacists is also available to walk you through dosage instructions and answer your questions. Reach out via phone or WhatsApp +2347065335797 or in-app messaging to get started.
It’s important to note that this information is not exhaustive, and if you or someone you know is concerned about fertility, it is recommended to consult a specialist for personalized advice and guidance.
References
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/getting-pregnant/in-depth/fertility/art-20047584
https://www.healthline.com/health/boost-male-fertility-sperm-count
https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-a-z/m/male-infertility