EARLY DETECTION OF PROSTATE CANCER

Prostate cancer remains one of the most common types of cancer affecting men. Early detection plays a pivotal role in improving treatment outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for those diagnosed. In this guide, we will explore why early detection is so important, discuss the primary screening methods including the Digital Rectal Exam (DRE) and Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) blood test, and highlight the benefits of regular screenings.
THE IMPORTANCE OF EARLY DETECTION OF PROSTATE CANCER
Why Early Detection Matters:
Early detection of prostate cancer is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, when prostate cancer is identified early, it is typically localized to the prostate gland. This localization means that treatment can be more straightforward and effective. For instance, treatments such as surgery or radiation therapy are often successful in curing or managing the disease at this stage [1]. The American Cancer Society reports that the 5-year survival rate for men with localized prostate cancer is nearly 100% [2]. This statistic underscores the significance of early diagnosis.
In addition, early detection helps in reducing the risk of complications. Prostate cancer that is detected and treated in its early stages is less likely to have spread to other parts of the body. This localized treatment approach minimizes the need for more aggressive therapies that are associated with greater side effects. As a result, patients may experience fewer complications and a better overall quality of life [3].
Furthermore, early detection allows for the management of the disease with fewer side effects. Advanced treatments such as hormone therapy or chemotherapy, which are used for later stages of cancer, can come with significant side effects, including fatigue and sexual dysfunction. By catching the cancer early, doctors can often use less invasive treatments, which can reduce the likelihood of experiencing these severe side effects [4].
SCREENING METHODS FOR PROSTATE CANCER
1. Digital Rectal Exam (DRE):
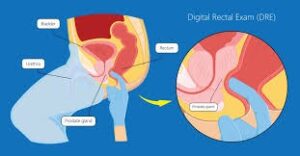
The Digital Rectal Exam (DRE) is a traditional screening method where a healthcare provider inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to examine the prostate gland. During the exam, the doctor checks for any abnormalities, such as lumps or hard areas, that might indicate the presence of cancer.
Advantages of the DRE:
- Direct Examination: The DRE allows for direct palpation of the prostate, which can help detect abnormalities that might suggest cancer [5]. This hands-on approach provides immediate, albeit limited, information.
- Simplicity and Speed: The DRE is a quick and straightforward procedure that can be performed during a routine visit to the doctor, making it an accessible option for many patients.
Limitations of the DRE:
- Limited Sensitivity: The DRE may not detect all prostate cancers, particularly those located in areas that are difficult to reach or in very early stages [6]. Consequently, some cancers may go unnoticed with this method alone.
- Variability in Results: The effectiveness of the DRE can vary depending on the experience of the doctor and the individual characteristics of the prostate gland [7]. This variability can sometimes lead to inconsistent results.
2. Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test:
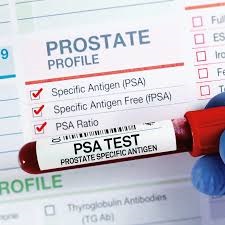
The PSA blood test measures the level of Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) in the blood. PSA is a protein produced by the prostate gland, and elevated levels can be a sign of prostate cancer, although other conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostatitis can also cause increased PSA levels [8].
Advantages of PSA Testing:
- Early Detection: The PSA test can identify elevated levels of PSA before any symptoms appear, making it a valuable tool for early diagnosis [9]. This early detection can lead to timely treatment.
- Quantitative Data: The test provides measurable data that can be tracked over time. This allows healthcare providers to monitor changes in PSA levels and assess the effectiveness of ongoing treatment [10].
Limitations of PSA Testing:
- False Positives and Negatives: Elevated PSA levels do not always indicate cancer, and normal PSA levels do not rule out the disease. This can lead to unnecessary anxiety and further testing [11]. Additionally, some cancers might not cause significant increases in PSA levels, leading to false negatives.
- Overdiagnosis: The PSA test can sometimes detect slow-growing cancers that might never cause significant problems. This can lead to overdiagnosis and overtreatment, which may cause unnecessary stress and potential side effects [12].
BENEFITS OF REGULAR SCREENING FOR PROSTATE CANCER

1. Improved Detection and Treatment:
Regular screening for prostate cancer increases the likelihood of detecting the disease early when it is most treatable. Early detection typically means that cancer is localized to the prostate and can be managed with less aggressive treatments. This can lead to better treatment outcomes and higher survival rates [13].
2. Tailored Health Management:
Consistent screening allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans based on individual patient data. By regularly monitoring PSA levels and conducting DREs, doctors can make informed decisions about treatment options and adjust them as necessary [14]. This personalized approach helps in optimizing treatment effectiveness and managing the disease more effectively.
3. Peace of Mind:
Regular screenings offer peace of mind by ensuring that any potential issues with prostate health are monitored and addressed promptly. Knowing that you are actively managing your health can reduce anxiety and stress related to potential cancer concerns [15]. This proactive approach helps maintain overall well-being and mental health.
4. Opportunity for Preventive Measures:
Routine screenings can help identify risk factors or conditions that may increase the likelihood of developing prostate cancer. Early identification of these risk factors allows for preventive measures, such as lifestyle changes or additional testing, to address potential issues before they become more serious [16]. This can help mitigate risks and improve long-term health outcomes.
MAKING AN INFORMED DECISION ABOUT SCREENING FOR PROSTATE CANCER

1. Discussing Risk Factors:
It is essential to have a discussion with your healthcare provider about your personal risk factors for prostate cancer. Factors such as age, family history, and any symptoms you may be experiencing can influence your decision about screening. Understanding these factors helps in determining the most appropriate timing and type of screening for you [17].
2. Weighing the Benefits and Risks:
Consider both the benefits and risks of prostate cancer screening. While early detection can lead to better outcomes, there are potential risks such as false positives and overdiagnosis. Discuss these factors with your healthcare provider to make an informed choice that aligns with your health goals and preferences [18].
3. Regular Follow-Up:
If you decide to undergo screening, regular follow-up is crucial for managing your health effectively. Consistent monitoring ensures that any changes in prostate health are addressed promptly and allows for adjustments to treatment plans as needed [19]. Regular check-ups help maintain optimal health and manage any emerging issues.
CONCLUSION.
Prostate cancer screening and early detection are vital components of effective disease management and improving overall health outcomes. By understanding the importance of early detection, familiarizing yourself with the screening methods available, and recognizing the benefits of regular screenings, you can make informed decisions about your prostate health.
The Digital Rectal Exam (DRE) and Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) blood test are essential tools for detecting prostate cancer early. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and they are often used together to provide a comprehensive assessment. Regular screenings offer numerous benefits, including early detection, personalized treatment, peace of mind, and opportunities for preventive measures.
By staying proactive with regular screenings and making informed decisions, you can effectively manage your prostate health and improve your long-term well-being.
REFERENCES:
- American Cancer Society. (2023). Prostate Cancer Survival Rates. Retrieved from American Cancer Society
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Prostate Cancer Treatment Options. Retrieved from Mayo Clinic
- National Cancer Institute. (2023). Prostate Cancer Statistics. Retrieved from National Cancer Institute
- Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Digital Rectal Exam (DRE) for Prostate Health. Retrieved from Cleveland Clinic
- American Urological Association. (2023). Limitations of DRE in Prostate Cancer Detection. Retrieved from AUA
- Prostate Cancer Foundation. (2023). Understanding PSA Testing. Retrieved from Prostate Cancer Foundation
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. (2023). PSA Testing and Prostate Cancer. Retrieved from NCCN
- Cancer Research UK. (2023). PSA Levels and Prostate Cancer. Retrieved from Cancer Research UK
- American Cancer Society. (2023). False Positives in PSA Testing. Retrieved from American Cancer Society
- The Lancet Oncology. (2023). Overdiagnosis in Prostate Cancer Screening. Retrieved from The Lancet Oncology
- Urology Care Foundation. (2023). Benefits and Risks of Prostate Cancer Screening. Retrieved from Urology Care Foundation
- Journal of Clinical Oncology. (2023). Prostate Cancer Detection and Management. Retrieved from Journal of Clinical Oncology
- Prostate Cancer Foundation. (2023). Prostate Cancer Early Detection Benefits. Retrieved from Prostate Cancer Foundation
- National Cancer Institute. (2023). Understanding Prostate Cancer Screening Options. Retrieved from National Cancer Institute
- American Cancer Society. (2023). Mental Health and Prostate Cancer. Retrieved from American Cancer Society
- American Institute for Cancer Research. (2023). Lifestyle Changes for Prostate Health. Retrieved from AICR
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. (2023). Prostate Cancer Risk Factors. Retrieved from NCCN
- Cancer Research UK. (2023). Balancing Benefits and Risks of Prostate Screening. Retrieved from Cancer Research UK
- Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Importance of Regular Prostate Check-ups. Retrieved from Cleveland Clinic