FEMALE INFERTILITY TREATMENTS

Female infertility is a challenge that affects many women and couples, often requiring various treatment strategies to achieve a successful pregnancy. Understanding the available treatments—ranging from medication and surgery to advanced assisted reproductive technologies (ART) like In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) and Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)—is crucial for making informed decisions. This guide will explore these treatment options, their success rates, and potential risks to help individuals and couples navigate their infertility journey.
OVERVIEW OF FEMALE INFERTILITY TREATMENT
Female infertility treatments are designed to address different underlying causes of infertility. Depending on the diagnosis, treatment options may vary. Common approaches include medication, surgical interventions, and assisted reproductive technologies (ART). Each treatment has its benefits, success rates, and associated risks.
MEDICATION FOR FEMALE INFERTILITY:
1. Ovulation Induction:
Ovulation induction is a common medication-based treatment for women who have difficulty ovulating. This approach is particularly beneficial for women with conditions such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) or hypothalamic dysfunction. The primary medications used for ovulation induction include:
- Clomiphene Citrate (Clomid): Clomid is often the first-line medication for inducing ovulation. It works by stimulating the pituitary gland to release hormones that promote egg development and ovulation. Success rates with Clomid are relatively high, with approximately 80% of women ovulating within three cycles. However, only about 30-40% of women will achieve pregnancy within six cycles.
- Letrozole (Femara): Originally used as a treatment for breast cancer, Letrozole is now also used off-label for ovulation induction. It works by lowering estrogen levels, which in turn stimulates the production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Studies have shown that Letrozole may be more effective than Clomid for some women, particularly those with PCOS.
- Gonadotropins: Gonadotropin injections, such as FSH or human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG), are used when oral medications are ineffective. These injections directly stimulate the ovaries to produce eggs. Gonadotropins can be highly effective but also come with a higher risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS).
2. Hormone Therapy:
Hormone therapy can be used to address hormonal imbalances that affect fertility. For example:
- Thyroid Hormone Replacement: Women with thyroid disorders may benefit from thyroid hormone replacement therapy to normalize thyroid levels and improve fertility.
- Progestin Supplements: For women with luteal phase defects (a condition where the uterine lining does not properly support implantation), progestin supplements may help support the endometrium and improve the chances of pregnancy.
SURGICAL TREATMENTS FOR FEMALE INFERTILITY:
1. Laparoscopy:
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat conditions that may affect fertility. It involves inserting a laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube) through a small incision in the abdomen. During laparoscopy, surgeons can:
- Remove Endometriosis: Endometriosis can cause significant pain and infertility by forming adhesions and scarring. Laparoscopic surgery can remove endometrial tissue and improve fertility outcomes.
- Treat Ovarian Cysts: Laparoscopy can be used to remove ovarian cysts that may interfere with ovulation and fertility.
- Address Tubal Blockages: In cases of blocked fallopian tubes, laparoscopy may involve procedures to open the tubes or repair any damage.
2. Hysteroscopy:
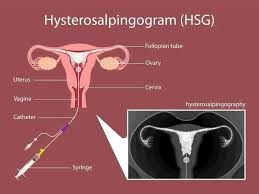
Hysteroscopy is another minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat uterine abnormalities. It involves inserting a hysteroscope through the vagina and cervix into the uterus. Common uses of hysteroscopy include:
- Removing Uterine Fibroids: Submucosal fibroids (fibroids that grow into the uterine cavity) can be removed using hysteroscopic surgery, which can enhance the likelihood of successful implantation.
- Correcting Septate Uterus: A septate uterus (a congenital abnormality where the uterus is divided by a septum) can be surgically corrected to improve fertility.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)used as method of treatment for infertility
1. Intrauterine Insemination (IUI):
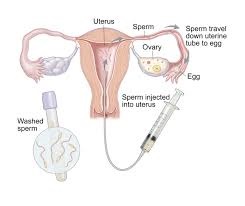
IUI is a relatively simple ART procedure where sperm is directly inserted into the uterus around the time of ovulation. This method is commonly used for couples with unexplained infertility, mild male factor infertility, or cervical issues. The process involves:
- Sperm Preparation: Sperm is collected and processed to concentrate and select the most motile sperm.
- Insemination: The prepared sperm is placed into the uterus using a thin catheter.
Success Rates: The success rates for IUI vary based on factors such as age and the underlying cause of infertility. Generally, the success rate per cycle ranges from 10-20%. Multiple cycles may be needed to achieve pregnancy.
Risks: The risks associated with IUI include multiple pregnancies (if fertility drugs are used), infection, and discomfort from the procedure.
2. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF):
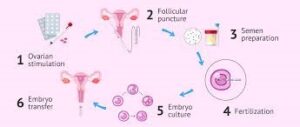
IVF is a more advanced ART technique that involves fertilizing eggs outside the body and then transferring the resulting embryos into the uterus. The IVF process typically includes:
- Ovarian Stimulation: Women undergo ovarian stimulation with medications to produce multiple eggs.
- Egg Retrieval: Eggs are retrieved from the ovaries using a needle guided by ultrasound.
- Fertilization: Eggs are combined with sperm in a laboratory setting to create embryos.
- Embryo Transfer: One or more embryos are transferred into the uterus.
Success Rates: IVF success rates vary based on age and other factors. On average, the success rate per IVF cycle ranges from 40% for women under 35 to around 10-20% for women over 40. Success rates improve with the use of preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) and embryo freezing.
Risks: Risks associated with IVF include ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), multiple pregnancies, and potential complications from the egg retrieval process.
3. Egg Donation and Gestational Surrogacy:
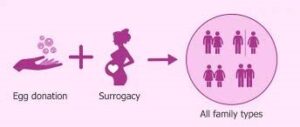
For women with diminished ovarian reserve or other issues preventing egg production, egg donation may be an option. Donor eggs are fertilized with the partner’s sperm or donor sperm and then transferred into the recipient’s uterus.
Gestational Surrogacy involves using a surrogate to carry a pregnancy for another individual or couple. In this process, an embryo created via IVF is implanted into the surrogate’s uterus.
Success Rates: Success rates for egg donation are generally high, with success rates similar to those of younger women using their own eggs. Gestational surrogacy also has high success rates, depending on the quality of the embryos and the health of the surrogate.
Risks: Risks include the physical and emotional impact on the egg donor or surrogate, legal and ethical considerations, and potential complications from the IVF process.
CONCLUSION.
Female infertility treatments offer a range of options tailored to different causes and individual needs. Medication, surgical interventions, and advanced assisted reproductive technologies like IUI and IVF provide various pathways to achieving pregnancy. Each treatment comes with its own success rates and potential risks, which should be carefully considered in consultation with healthcare professionals.
REFERENCES:
- American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM). (n.d.). Infertility Treatment Options
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2022). Assisted Reproductive Technology
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Female Infertility Treatments