LUNG CANCER TREATMENTS: YOUR OPTIONS
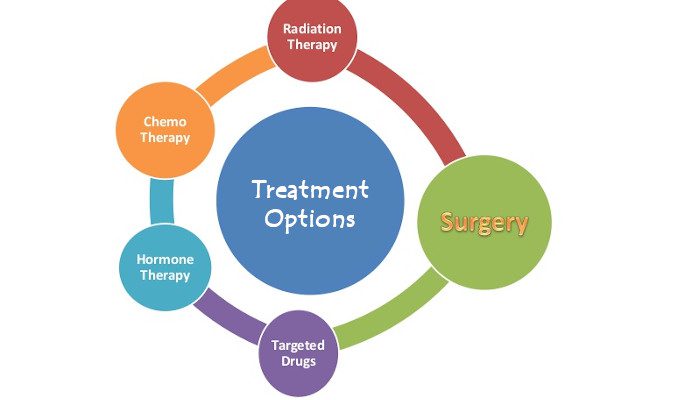
Lung cancer treatment has evolved significantly over the years, offering various approaches to manage the disease effectively. From surgery and chemotherapy to radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, each treatment option plays a critical role in addressing lung cancer. This comprehensive guide will explore these treatment options, discuss how treatment choices are made based on cancer stage and patient health, and highlight the importance of palliative care for those with advanced-stage lung cancer.
1. UNDERSTANDING LUNG CANCER TREATMENT OPTIONS.
When it comes to treating lung cancer, several options are available, each tailored to the specific needs of the patient. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the type and stage of cancer, the patient’s overall health, and their personal preferences. Below, we delve into the main treatment approaches used for lung cancer.
1.1 Surgery
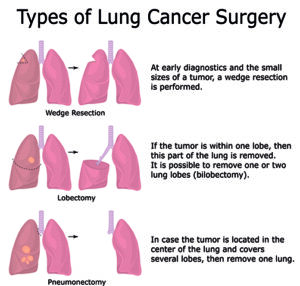
Illustration of three types of lung cancer surgery with descriptions
Surgery is often the first-line treatment for early-stage lung cancer. The primary goal of surgery is to remove the tumor and any affected tissue from the lung. There are different types of surgical procedures used:
- Lobectomy: This involves the removal of one lobe of the lung where the cancer is located. It is the most common surgical approach for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
- Pneumonectomy: This procedure entails the removal of an entire lung. It is generally considered when the cancer is confined to one lung and cannot be treated with a lobectomy.
- Wedge Resection: A wedge resection involves removing a small portion of the lung that contains the tumor, along with some surrounding healthy tissue. This option is typically used for smaller tumors or when the patient has reduced lung function.
1.2 Chemotherapy
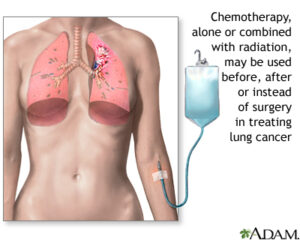
Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. This treatment is often used when lung cancer has spread beyond the lungs or when surgery is not an option. Chemotherapy can be administered in various ways:
- Intravenous (IV) Infusion: Chemotherapy drugs are delivered directly into the bloodstream through an IV line. This method allows the drugs to circulate throughout the body and target cancer cells.
- Oral Medications: Some chemotherapy drugs can be taken in pill form. These are usually used in combination with IV drugs for more comprehensive treatment.
Chemotherapy can have side effects, such as nausea, hair loss, and fatigue. However, these side effects are often manageable and temporary.
1.3 Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It is typically used for patients who cannot undergo surgery or as an adjunct treatment to help eliminate remaining cancer cells after surgery. There are two main types of radiation therapy:
- External Beam Radiation Therapy: This method directs radiation from outside the body towards the tumor. It is the most common type of radiation therapy for lung cancer.
- Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT): SBRT delivers high doses of radiation with precision to a small, targeted area. It is often used for small, localized tumors.
1.4 Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth and survival. This approach can be particularly effective for certain types of lung cancer that have specific genetic mutations. Targeted therapy drugs can block the growth of cancer cells by interfering with these molecular targets. Common types of targeted therapy include:
- EGFR Inhibitors: These drugs target mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene, which is involved in cell growth and division.
- ALK Inhibitors: These drugs target abnormalities in the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene, which can drive cancer growth.
1.5 Immunotherapy
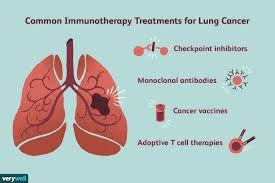
Immunotherapy works by boosting the body’s natural defenses to fight cancer. It is a newer approach that harnesses the power of the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Some common types of immunotherapy for lung cancer include:
- Checkpoint Inhibitors: These drugs block proteins that prevent immune cells from attacking cancer cells. Examples include pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and nivolumab (Opdivo).
- CAR-T Cell Therapy: This approach involves modifying a patient’s T cells to better recognize and attack cancer cells. Although more commonly used for other cancers, research is ongoing for its use in lung cancer.
2. CHOOSING THE RIGHT TREATMENT FOR LUNG CANCER

The choice of treatment for lung cancer depends on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the type of lung cancer, and the patient’s overall health.
2.1 Stage of Cancer
Early-Stage Lung Cancer: For cancers detected at an early stage, surgery is often the preferred treatment. Depending on the size and location of the tumor, a lobectomy or wedge resection may be recommended. In some cases, radiation therapy may be used if surgery is not feasible.
Advanced-Stage Lung Cancer: For cancers that have spread beyond the lungs, treatment typically involves a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. The choice of treatment depends on the specific characteristics of the cancer and how well the patient tolerates the treatments.
2.2 Patient’s Overall Health
The patient’s overall health and ability to tolerate treatment play a crucial role in determining the appropriate approach. For example, patients with other health conditions may not be able to undergo aggressive treatments like surgery or chemotherapy and may require alternative options like targeted therapy or palliative care.
3. PALLIATIVE CARE FOR ADVANCED-STAGE LUNG CANCER
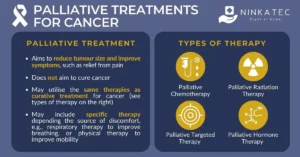
For patients with advanced-stage lung cancer, palliative care plays a crucial role in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Unlike curative treatments, palliative care focuses on relieving symptoms and providing comfort, regardless of the stage of cancer.
3.1 Objectives of Palliative Care
Symptom Management: Palliative care aims to manage symptoms such as pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. This may involve medications, therapies, and supportive care measures.
Emotional and Psychological Support: Dealing with advanced cancer can be emotionally challenging. Palliative care includes psychological support to help patients and their families cope with the emotional aspects of the disease.
Coordination of Care: Palliative care teams work closely with other healthcare providers to ensure that all aspects of the patient’s care are addressed, including treatment side effects and supportive services.
3.2 Benefits of Palliative Care
Improved Quality of Life: Palliative care can significantly enhance the quality of life by addressing symptoms and providing support, allowing patients to focus on their well-being and comfort.
Family Support: Palliative care provides support to family members, helping them navigate the challenges of caregiving and providing them with resources and guidance.
CONCLUSION.
Lung cancer treatment options are diverse, and the choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the stage of cancer and the patient’s overall health. Understanding the available treatment approaches—surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy—can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions.
For those with advanced-stage lung cancer, palliative care is essential in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. It provides comprehensive support to both patients and their families, ensuring that comfort and emotional well-being are prioritized.
If you or a loved one is facing a lung cancer diagnosis, consult with healthcare professionals to explore the best treatment options for your specific situation. Staying informed and proactive is key to navigating the complexities of lung cancer treatment and achieving the best possible outcomes.
REFERENCES:
- American Cancer Society (ACS). (2023). “Lung Cancer Surgery.” Link
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). “Lung Cancer Surgery Overview.” Link
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). (2023). “Chemotherapy for Lung Cancer.” Link
- American Cancer Society (ACS). (2023). “Chemotherapy for Lung Cancer.” Link
- American Cancer Society (ACS). (2023). “Radiation Therapy for Lung Cancer.” Link
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). “Radiation Therapy for Lung Cancer.” Link
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). (2023). “Targeted Therapy for Lung Cancer.” Link
- American Cancer Society (ACS). (2023). “Targeted Therapy for Lung Cancer.” Link
- American Cancer Society (ACS). (2023). “Immunotherapy for Lung Cancer.” Link
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). (2023). “Immunotherapy for Lung Cancer.” Link
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). (2023). “Lung Cancer Treatment Guidelines.” Link
- American Cancer Society (ACS). (2023). “Lung Cancer Treatment by Stage.” Link
- American Cancer Society (ACS). (2023). “Palliative Care for Lung Cancer.” Link
- National Institute on Aging (NIA). (2023). “Palliative Care: What is it and Why is it Important?” Link
- American Cancer Society (ACS). (2023). “Lung Cancer Treatment Overview.” Link
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). (2023). “Lung Cancer Treatment.” Link