PREVENTING OVARIAN CANCER

Ovarian cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that affects thousands of women each year. While it is crucial to understand the challenges associated with ovarian cancer, it is equally important to explore strategies for prevention and risk reduction. This guide delves into the various methods for reducing the risk of ovarian cancer, including the use of birth control pills, tubal ligation, and hysterectomy. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of awareness regarding ovarian cancer risk factors and the value of early detection.
THE IMPORTANCE OF RISK REDUCTION STRATEGIES OF DEVELOPING OVARIAN CANCER
Risk reduction strategies play a vital role in lowering the likelihood of developing cancer of the ovary. By understanding and implementing these strategies, individuals can take proactive steps towards safeguarding their health.
1. Birth Control Pills:
Birth control pills, also known as oral contraceptives, have been shown to have a protective effect against ovarian cancer. Several studies have indicated that the use of birth control pills reduces the risk of ovarian cancer by up to 30% to 50% [1].
How Birth Control Pills Help:
- Hormonal Regulation: Birth control pills regulate menstrual cycles and reduce the number of ovulations a woman experiences over her lifetime. Each ovulation is associated with a small risk of ovarian cancer, so fewer ovulations mean a reduced risk [2].
- Long-Term Protection: The protective effect of birth control pills persists for many years after discontinuation. Research has shown that women who have used oral contraceptives for several years have a lower risk of ovarian cancer even after they stop using them [3].
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if birth control pills are an appropriate option based on individual health needs and risk factors.
2. Tubal Ligation:
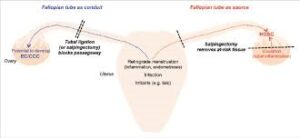
Tubal ligation, commonly referred to as “tying the tubes,” is a surgical procedure that involves closing or sealing the fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy. This procedure has also been associated with a reduced risk of ovarian cancer.
Benefits of Tubal Ligation:
- Reduced Risk: Studies have shown that tubal ligation can lower the risk of ovarian cancer by approximately 30% to 50% [4]. The mechanism behind this is not entirely clear, but it is believed that the procedure may reduce the risk by decreasing the number of menstrual cycles and changing the hormonal environment in the ovaries.
- Permanent Contraception: Tubal ligation provides a permanent form of contraception, which may be appealing for women who do not wish to have more children.
As with any surgical procedure, it’s essential to discuss the benefits and potential risks with a healthcare provider to ensure it aligns with personal health goals and circumstances.
3. Hysterectomy:
A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the uterus. In some cases, a hysterectomy may also include the removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy). Removing the ovaries as part of a hysterectomy can significantly reduce the risk of the said cancer, particularly in women with a high genetic risk.
Types of Hysterectomy:
- Total Hysterectomy: This involves the removal of the uterus and cervix but leaves the ovaries in place. While this procedure is often performed for other health reasons, it does not impact the risk of ovarian cancer.
- Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy: This involves the removal of both ovaries and fallopian tubes. This procedure is typically recommended for women at high risk of the above discussed cancer, such as those with BRCA1 or BRCA2 genetic mutations [5].
Risk Reduction: Women who undergo bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy significantly lower their risk of developing cancer of the ovary. However, this procedure also induces menopause, which can have other health implications, so it should be considered carefully [6].
RAISING AWARENESS OF OVARIAN CANCER RISK FACTORS
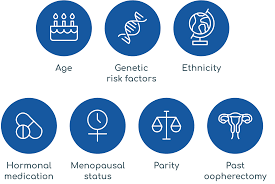
Awareness of ovarian cancer risk factors is crucial for early detection and prevention. By understanding these factors, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and take proactive steps to reduce their risk.
1. Genetic Factors:
Genetics play a significant role in ovarian cancer risk. Women with a family history of ovarian cancer or breast cancer may be at higher risk due to genetic mutations.
- BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations: Women with BRCA1 or BRCA2 genetic mutations have a significantly higher risk of developing the said cancer. Testing for these mutations can help determine if a woman is at increased risk [7].
- Family History: A strong family history of ovarian or breast cancer can also indicate an increased risk. Genetic counseling and testing may be recommended for women with a family history of these cancers [8].
2. Reproductive History:
Reproductive history can influence the cancer of the ovary’s risk. Factors such as age at first menstruation, number of pregnancies, and age at menopause can impact risk levels.
- Early Menstruation and Late Menopause: Women who experience early onset of menstruation or late onset of menopause have a longer exposure to hormones, which may increase their risk of ovarian cancer [9].
- Pregnancies and Childbirth: Women who have had multiple pregnancies and childbirths tend to have a lower risk of ovarian cancer. Pregnancy and breastfeeding reduce the number of ovulations a woman has, thereby lowering her risk [10].
3. Lifestyle Factors:
Certain lifestyle factors can also influence ovarian cancer risk. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall health and may reduce the risk of various cancers, including ovarian cancer.
- Diet and Exercise: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with regular physical activity, can support overall health and may help in reducing cancer risk [11].
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can also contribute to a lower risk of cancer [12].
ENCOURAGING EARLY DETECTION OF OVARIAN CANCER

Early detection of this cancer can significantly improve treatment outcomes and survival rates. Several strategies can help in detecting ovarian cancer at an early stage.
1. Regular Check-Ups:
Regular gynecological check-ups are essential for monitoring ovarian health. During these visits, healthcare providers can perform pelvic exams and discuss any symptoms or concerns.
- Pelvic Exams: Routine pelvic exams can help identify abnormal changes in the ovaries. Although pelvic exams alone cannot diagnose ovarian cancer, they are an important part of regular health checks [13].
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: For women with symptoms or risk factors, a transvaginal ultrasound may be used to examine the ovaries for any abnormalities [14].
2. CA-125 Blood Test:
The CA-125 blood test measures the level of the CA-125 protein in the blood, which can be elevated in women with cancer of the ovary. However, this test is not specific to the cancer of the ovary and may also be elevated due to other conditions.
- Use in High-Risk Women: The CA-125 test is often used in combination with other diagnostic tools for women at high risk or those with symptoms suggestive of ovarian cancer [15].
- Limitations: The CA-125 test is not typically used for routine screening in the general population due to its limitations. It is more useful in monitoring patients who have already been diagnosed with ovarian cancer [16].
CONCLUSION.
Ovarian cancer prevention and risk reduction are vital aspects of managing women’s health. Strategies such as using birth control pills, undergoing tubal ligation, and considering hysterectomy can significantly reduce the risk of getting this cancer. Additionally, awareness of risk factors and the importance of early detection play crucial roles in improving outcomes and reducing mortality.
By understanding and implementing these preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps toward reducing their risk of getting the above said cancer. Regular check-ups, awareness of genetic risks, and a healthy lifestyle all contribute to effective prevention and early detection. It is essential for women to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized plan for risk reduction and to stay informed about the latest advancements in ovarian cancer research and prevention.
REFERENCES:
- American Cancer Society. (2023). Birth Control Pills and Ovarian Cancer Risk. Retrieved from American Cancer Society
- National Cancer Institute. (2022). Oral Contraceptives and Ovarian Cancer. Retrieved from National Cancer Institute
- Cancer Research UK. (2023). Long-Term Effects of Birth Control on Ovarian Cancer Risk. Retrieved from Cancer Research UK
- Society of Gynecologic Oncology. (2023). Tubal Ligation and Ovarian Cancer Risk. Retrieved from SGO
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Hysterectomy and Ovarian Cancer Risk Reduction. Retrieved from Mayo Clinic
- Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy for Ovarian Cancer Prevention. Retrieved from Cleveland Clinic
- BRCA Foundation. (2023). Genetic Testing and Ovarian Cancer Risk. Retrieved from BRCA Foundation
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. (2023). Family History and Ovarian Cancer Risk. Retrieved from NCCN
- The Lancet Oncology. (2022). Reproductive History and Ovarian Cancer Risk. Retrieved from The Lancet Oncology
- Cancer Support Community. (2023). Pregnancy and Ovarian Cancer Risk. Retrieved from Cancer Support Community
- American Institute for Cancer Research. (2023). Diet and Physical Activity in Cancer Prevention. Retrieved from AICR
- National Institute on Drug Abuse. (2023). Smoking, Alcohol, and Cancer Risk. Retrieved from NIDA
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Pelvic Exam for Ovarian Health. Retrieved from Mayo Clinic
- National Cancer Institute. (2023). Transvaginal Ultrasound for Ovarian Cancer. Retrieved from National Cancer Institute
- American Cancer Society. (2023). CA-125 Blood Test and Ovarian Cancer. Retrieved from American Cancer Society
- Cancer Research UK. (2023). Limitations of the CA-125 Test. Retrieved from Cancer Research UK