CATCHING OVARIAN CANCER EARLY
Ovarian cancer is a significant health concern for women worldwide. Its high mortality rate is primarily due to the disease often being diagnosed at an advanced stage. Consequently, early detection plays a crucial role in improving survival rates and treatment outcomes. In this article, we will discuss the importance of early detection, explore various screening methods such as pelvic exams, transvaginal ultrasounds, and CA-125 blood tests, and highlight the challenges associated with early detection.
THE IMPORTANCE OF EARLY DETECTION OF OVARIAN CANCER

Early detection of ovarian cancer is vital for several reasons. First and foremost, when ovarian cancer is detected at an early stage, the chances of successful treatment and survival significantly increase. According to the American Cancer Society, the five-year survival rate for women with ovarian cancer diagnosed at an early stage is approximately 93%, compared to only 30% for those diagnosed at a late stage [1]. This stark difference underscores the critical need for effective early detection strategies.
Moreover, early detection can lead to less aggressive treatment options. When ovarian cancer is caught early, treatments such as surgery and chemotherapy can be less invasive and more effective. For instance, early-stage ovarian cancer often requires only surgery to remove the tumor, whereas advanced stages may necessitate more extensive surgery combined with aggressive chemotherapy [2].
SCREENING METHODS TO DETECT OVARIAN CANCER
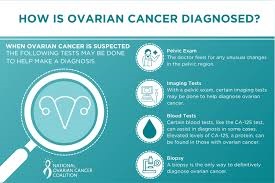
Several screening methods are utilized to detect ovarian cancer early. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and understanding these can help in choosing the most appropriate approach for individual patients.
1. Pelvic Exams:
Pelvic exams are a fundamental part of routine gynecological check-ups. During a pelvic exam, a healthcare provider palpates the ovaries to check for any abnormalities. This method is simple and non-invasive, making it a commonly used screening tool. However, pelvic exams have limitations. They are not highly sensitive or specific for detecting ovarian cancer. According to research, pelvic exams can miss small tumors and are not reliable in identifying ovarian cancer at its earliest stage [3].
2. Transvaginal Ultrasound:
Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) is another screening method used for ovarian cancer. This technique involves inserting a small probe into the vagina to produce detailed images of the ovaries. TVUS can help detect abnormalities such as cysts or tumors in the ovaries. It is more effective than pelvic exams in identifying ovarian masses. However, TVUS is not perfect. It can sometimes produce false positives, leading to unnecessary anxiety and additional testing [4].
3. CA-125 Blood Test:
The CA-125 blood test measures the level of a protein called CA-125 in the blood. Elevated levels of CA-125 can be indicative of ovarian cancer, as this protein is often present in higher amounts in women with ovarian cancer. The CA-125 test is useful for monitoring treatment progress and detecting recurrence in women already diagnosed with ovarian cancer. Nonetheless, CA-125 is not specific to ovarian cancer and can be elevated in other conditions such as endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease. Therefore, it is not a standalone test for early detection [5].
CHALLENGES OF EARLY DETCTION OF OVARIAN CANCER
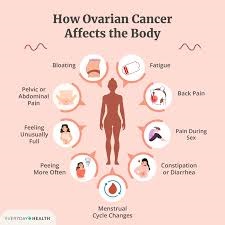
Despite advancements in screening methods, early detection of ovarian cancer remains challenging. Several factors contribute to these challenges:
1. Lack of Specific Symptoms:
One of the primary difficulties in detecting ovarian cancer early is the lack of specific symptoms. Often, the symptoms of ovarian cancer, such as bloating, pelvic pain, and frequent urination, are nonspecific and can be attributed to other, less serious conditions. This means that by the time symptoms become noticeable, the cancer may already be at an advanced stage [6].
2. Low Screening Sensitivity:
Currently available screening methods have varying degrees of sensitivity and specificity. While transvaginal ultrasound and CA-125 blood tests can help in identifying ovarian abnormalities, they are not foolproof. The sensitivity of these tests in detecting early-stage ovarian cancer is limited. For instance, transvaginal ultrasound may not detect small tumors, and CA-125 levels can be elevated due to other non-cancerous conditions [7].
3. High Rate of False Positives:
Screening methods such as CA-125 blood tests and transvaginal ultrasounds can produce false positive results. A false positive occurs when a test indicates the presence of cancer when there is none. This can lead to unnecessary worry, additional invasive procedures, and increased healthcare costs. In some cases, false positives may also result in overdiagnosis, where benign conditions are mistakenly treated as cancerous [8].
4. Lack of a Comprehensive Screening Protocol:
Currently, there is no universally accepted comprehensive screening protocol for ovarian cancer. While methods like pelvic exams, transvaginal ultrasounds, and CA-125 tests are used, there is no single screening test recommended for all women. This lack of a standardized approach means that screening strategies can vary widely, leading to inconsistencies in early detection [9].
CONCLUSION.
Early detection of ovarian cancer is crucial for improving survival rates and treatment outcomes. While methods such as pelvic exams, transvaginal ultrasounds, and CA-125 blood tests play important roles in screening, each has its limitations. The challenges of early detection, including nonspecific symptoms, low test sensitivity, high false positive rates, and the absence of a standardized screening protocol, underscore the need for continued research and development in this area.
Efforts to improve early detection are ongoing. Researchers are exploring new biomarkers and advanced imaging techniques to enhance the accuracy of ovarian cancer screening. For now, women should engage in regular check-ups with their healthcare providers, especially if they have a family history of ovarian cancer or other risk factors. Early detection and intervention remain key to fighting this challenging disease.
REFERENCES:
- American Cancer Society. (2023). Ovarian Cancer Survival Rates by Stage. Retrieved from American Cancer Society
- National Cancer Institute. (2022). Treatment for Ovarian Cancer. Retrieved from National Cancer Institute
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. (2018). Screening for Ovarian Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA, 319(6), 588-594.
- Society of Gynecologic Oncology. (2023). Transvaginal Ultrasound and Ovarian Cancer. Retrieved from Society of Gynecologic Oncology
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). CA-125 Blood Test. Retrieved from Mayo Clinic
- Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Ovarian Cancer Symptoms. Retrieved from Cleveland Clinic
- Cancer Research UK. (2022). Ovarian Cancer Screening. Retrieved from Cancer Research UK
- The Lancet Oncology. (2021). Challenges in Ovarian Cancer Screening and Management. Retrieved from The Lancet Oncology
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2023). Screening for Ovarian Cancer. Retrieved from ACOG